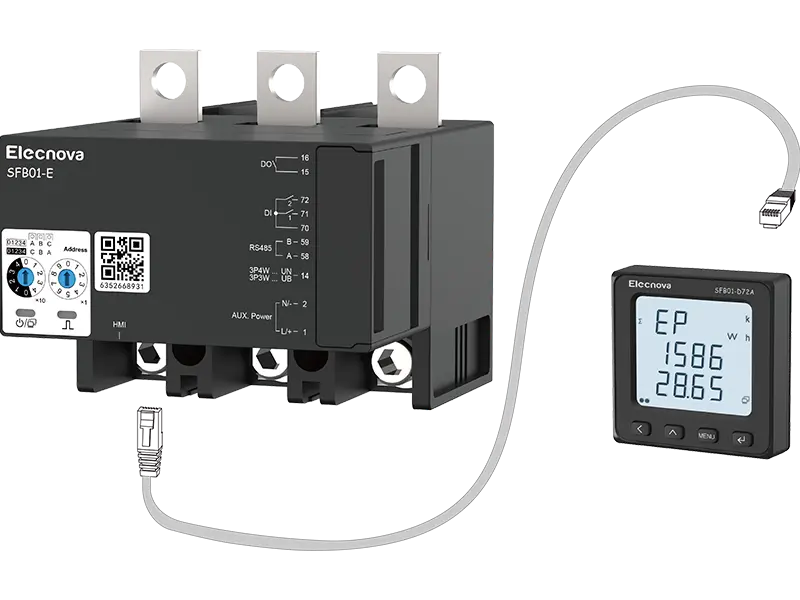
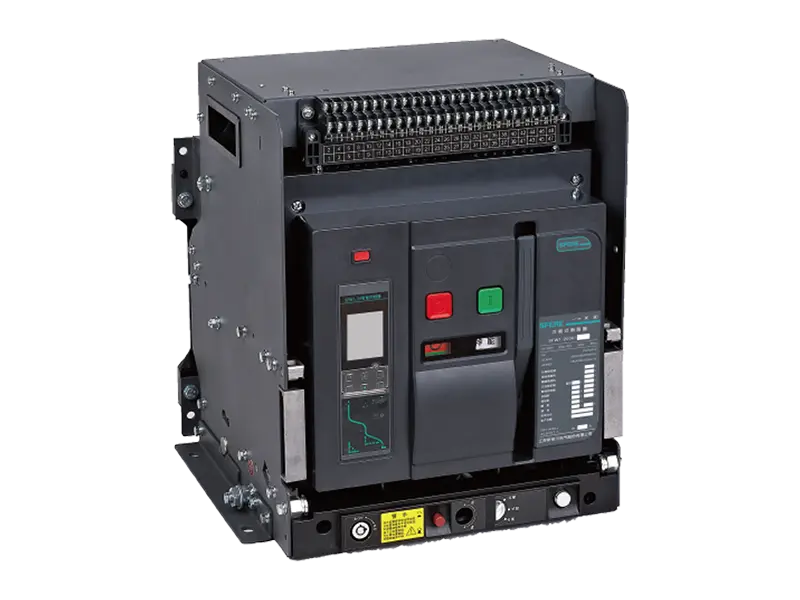
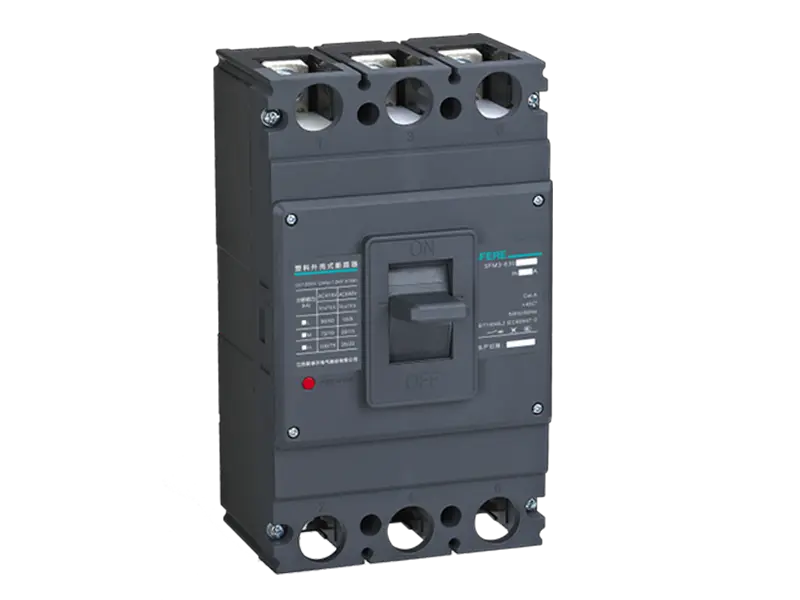
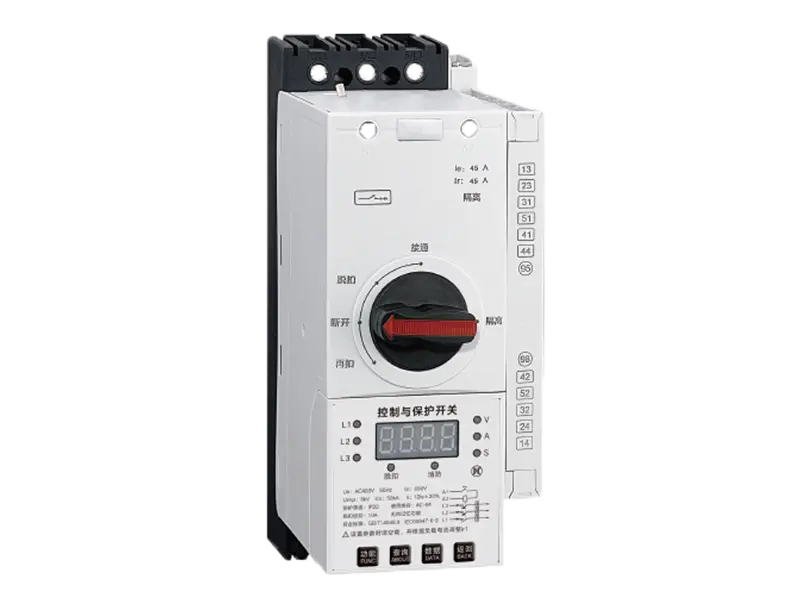
- Smart Meter
- Multi-Functional Power Meter
- Digital Power Meter
- Intelligent Electrical Transducer
- Multi-circuit Monitoring Unit
- Multi-Circuit Power Meter
- Precision Power Distribution Unit
- Motor Protection Controller
- Microcomputer Integrated Protection Device
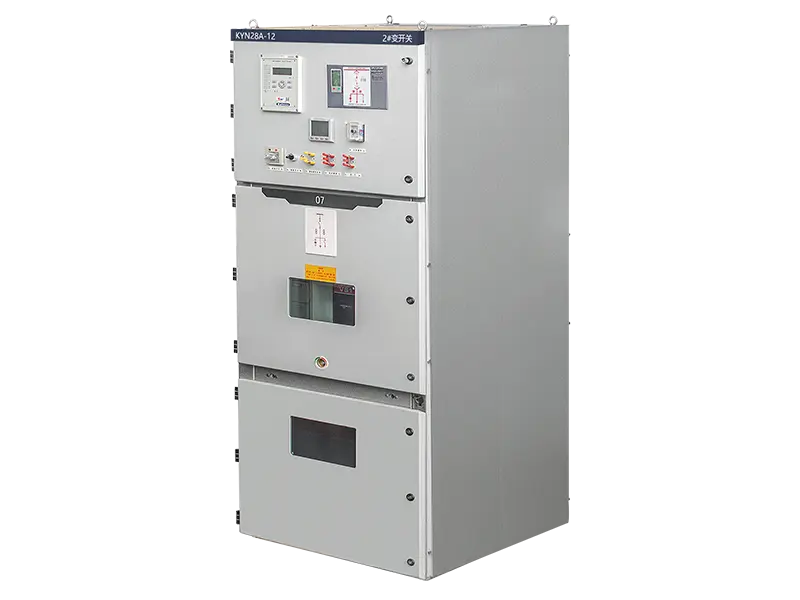
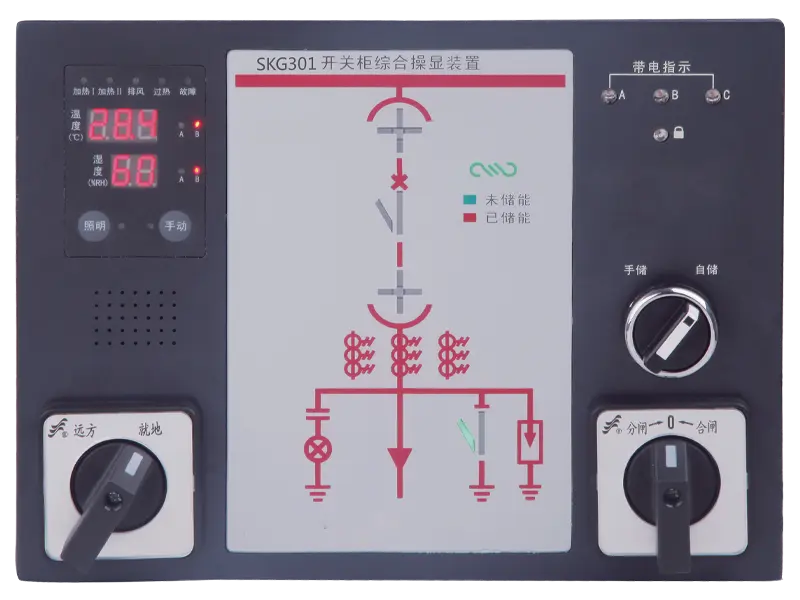
- Intelligent Control Device for Switch Cabinet
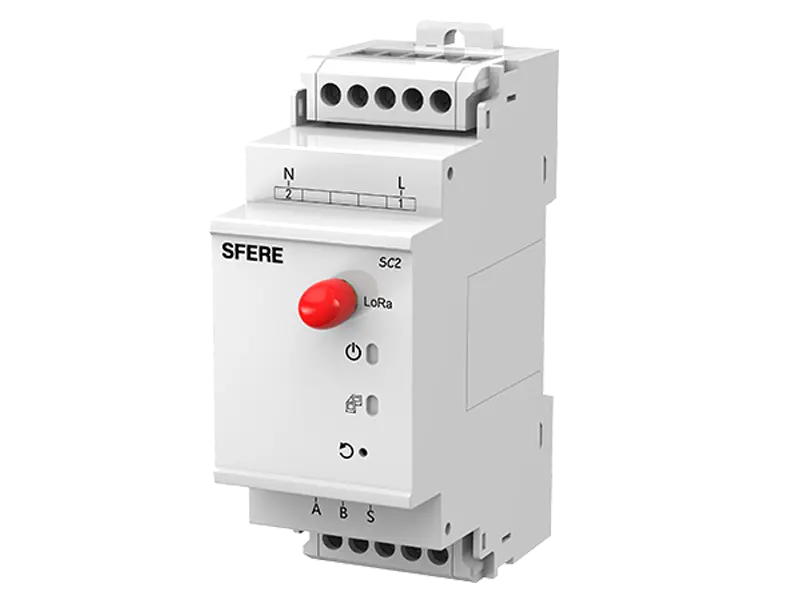
- Communication Gateway
- Rack-Mounted Busway Monitoring Unit
- Current Transformer
- Integrated Multi-functional Power Meter
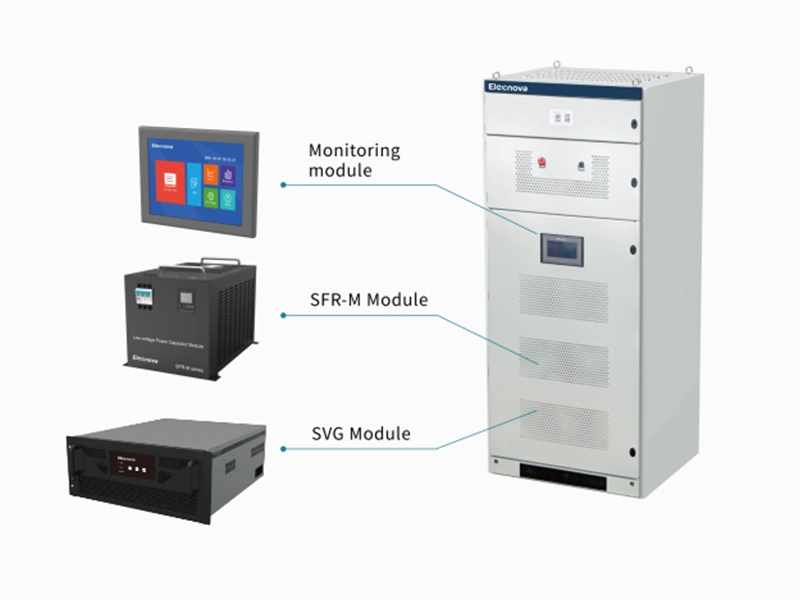
- Active Harmonic Filter (APF)
- Static Var Generator (SVG)
- Smart Capacitor Bank
- Harmonic Mitigation & Reactive Compensation Component
- Switch & Control Unit
- Intelligent Power Quality Management Software
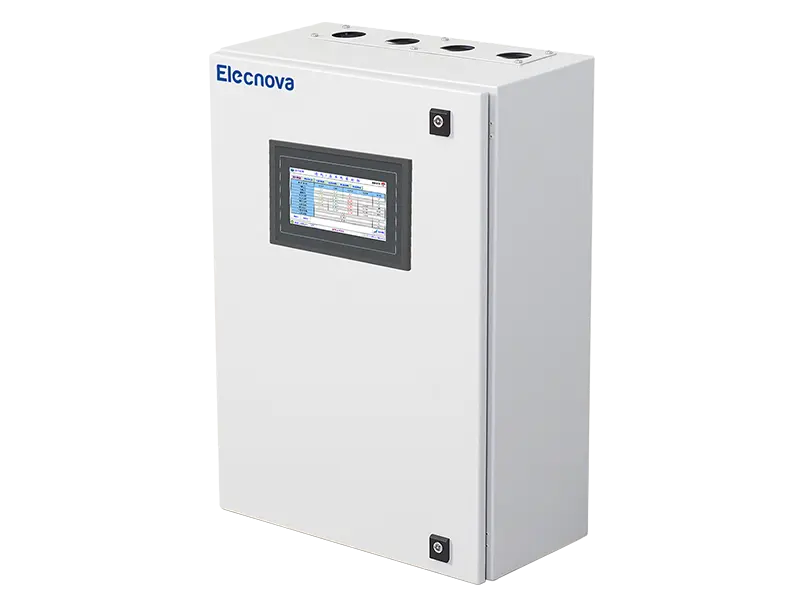
- Power Quality Monitoring Cabinet
- Intelligent Measuring Terminal for Electrical Safety
- Electrical Fire Monitoring System
- Fire Fighting Equipment Power Monitoring System
- Fire Door Monitoring System
- Temperature Monitoring System
- Surge Protection Device

English
What are you looking for?