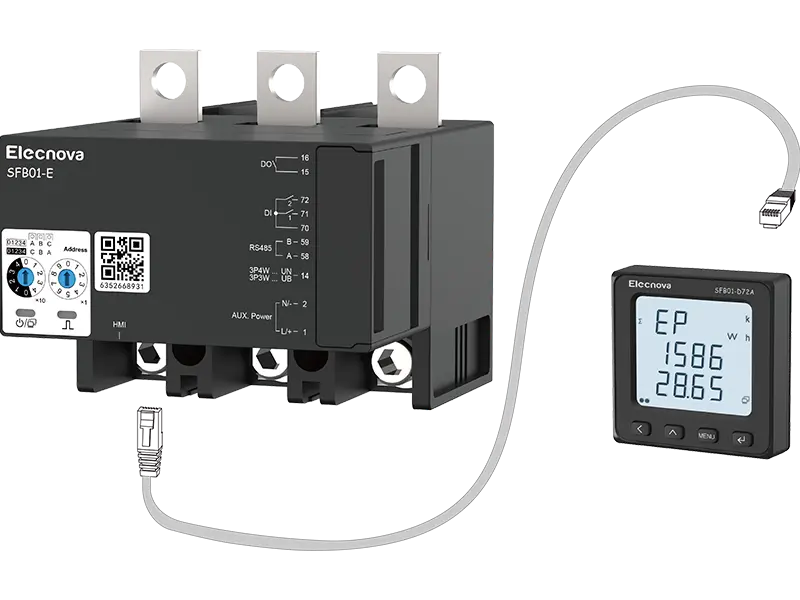
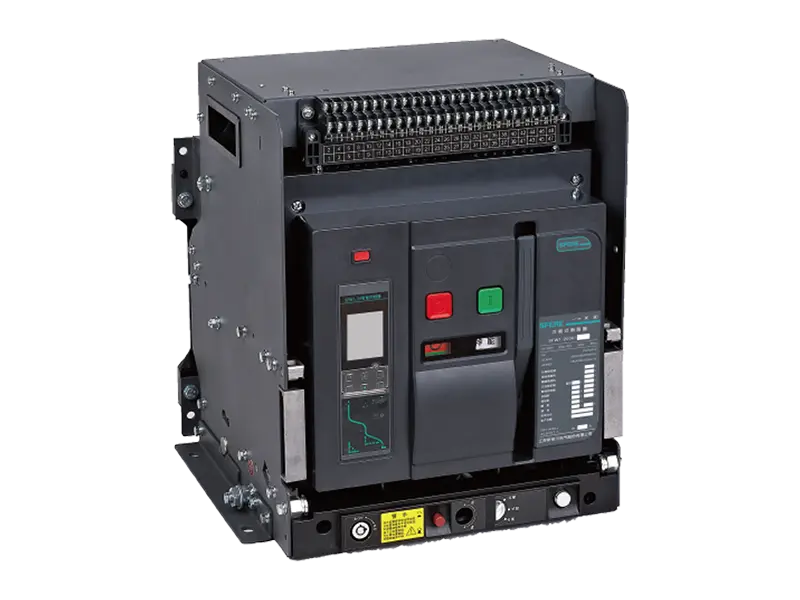
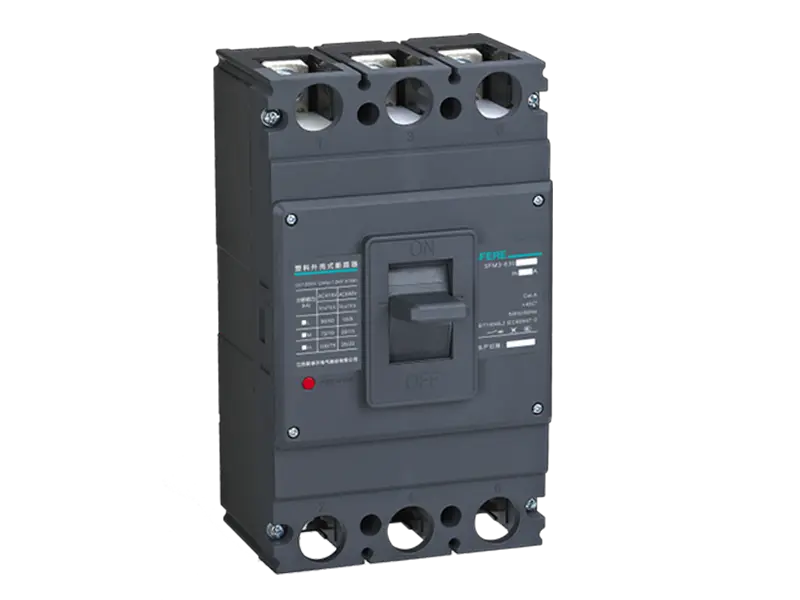
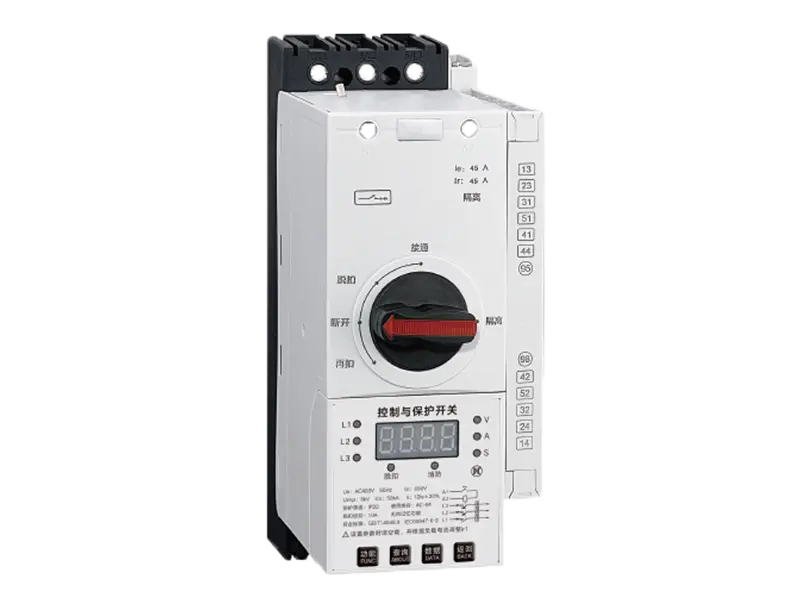
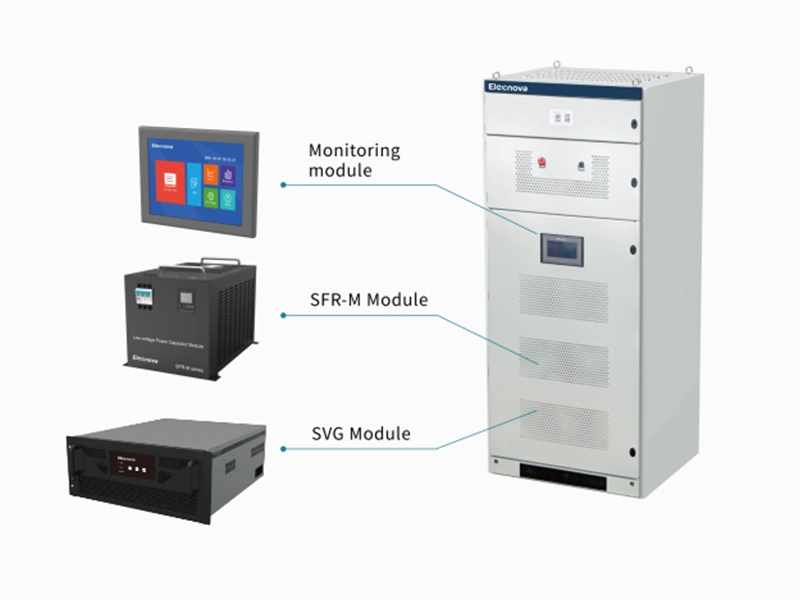
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) are electrical protection devices designed to safeguard electrical circuits and equipment from overloads, short circuits, and other faults. They come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and requirements. Here are some common types of MCCBs:
1. Thermal-Magnetic MCCBs: These MCCBs combine thermal and magnetic tripping mechanisms to provide comprehensive protection against both overloads and short circuits. The thermal element responds to sustained overcurrents, while the magnetic element reacts quickly to short-circuit currents, ensuring fast and reliable circuit interruption.
2. Electronic MCCBs: Electronic MCCBs utilize solid-state electronic trip units instead of traditional thermal-magnetic elements. They offer enhanced precision, flexibility, and adjustability in trip settings, allowing for precise coordination and customization of protection curves. Electronic MCCBs are suitable for applications requiring advanced protection features and selective coordination.
3. Adjustable MCCBs: Adjustable MCCBs allow users to adjust the tripping characteristics, such as current rating and trip curve, to match specific application requirements. These MCCBs offer flexibility and versatility in protection settings, making them suitable for a wide range of applications where customized protection is needed.
4. Non-Adjustable MCCBs: Non-adjustable MCCBs have fixed tripping characteristics and cannot be adjusted by the user. They offer simplicity and reliability in protection settings, making them suitable for applications where standard protection requirements apply and customization is not necessary.
5. High-Performance MCCBs: High-performance MCCBs are designed to withstand harsh environments, high fault currents, and extreme operating conditions. They feature robust construction, advanced materials, and enhanced protection capabilities to ensure reliable operation in demanding applications such as industrial plants, utility substations, and critical infrastructure installations.
6. Compact MCCBs: Compact MCCBs are designed for space-constrained applications where size and footprint are critical factors. They feature a compact and lightweight design while providing reliable protection and performance, making them suitable for use in switchgear, control panels, and other confined spaces.
Overall, the choice of MCCB type depends on factors such as application requirements, operating conditions, and desired features, with each type offering specific advantages and capabilities to meet various protection needs.