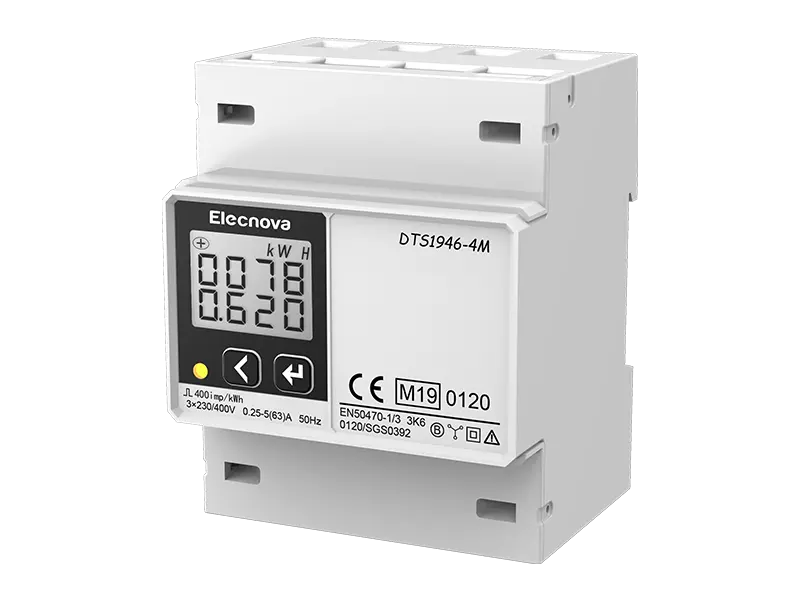
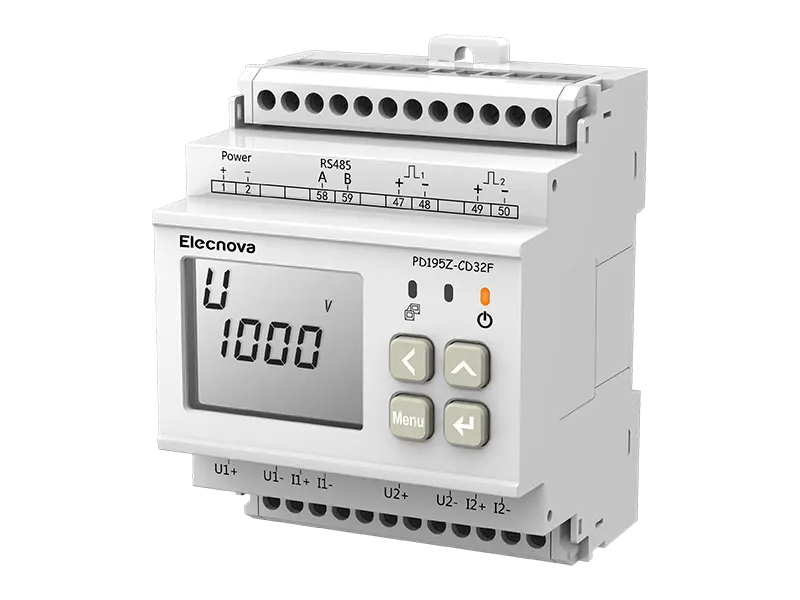
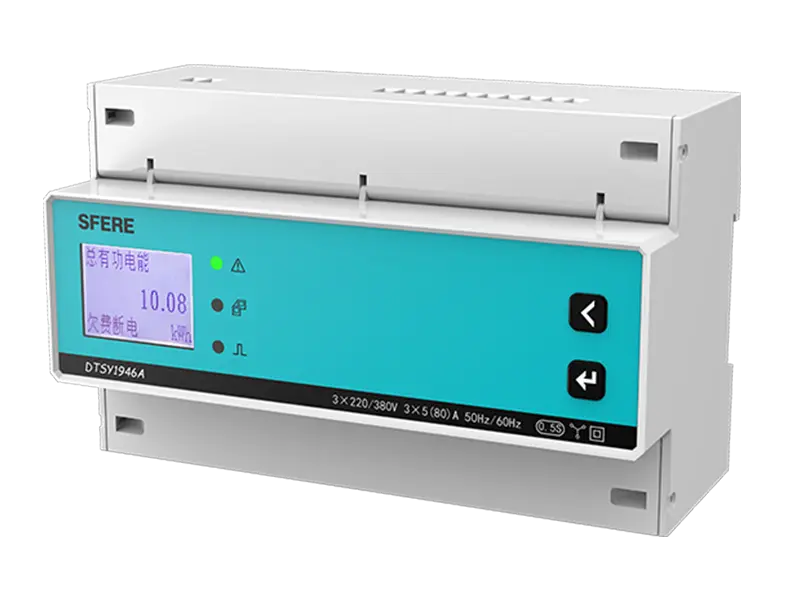
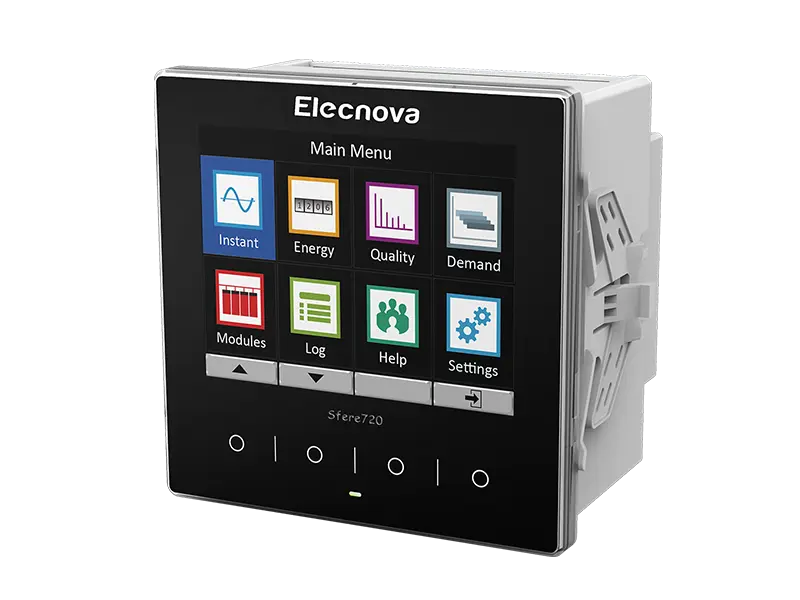
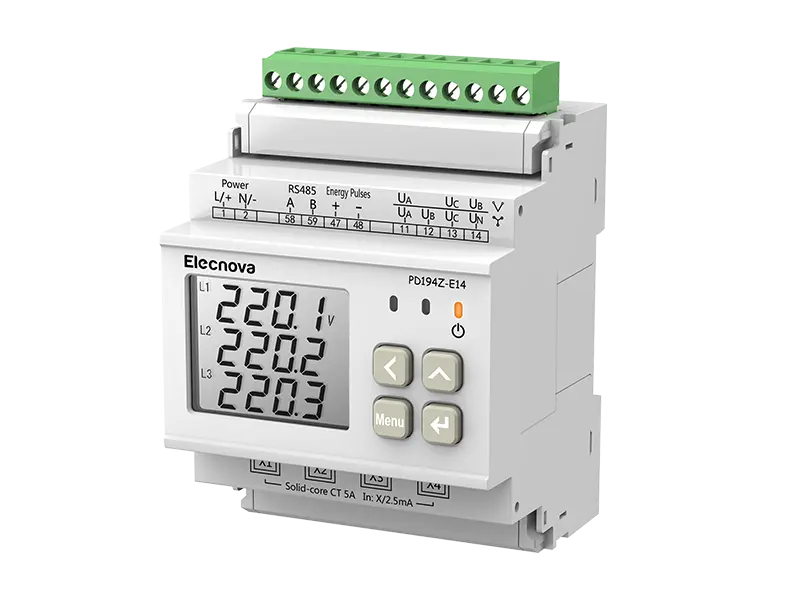
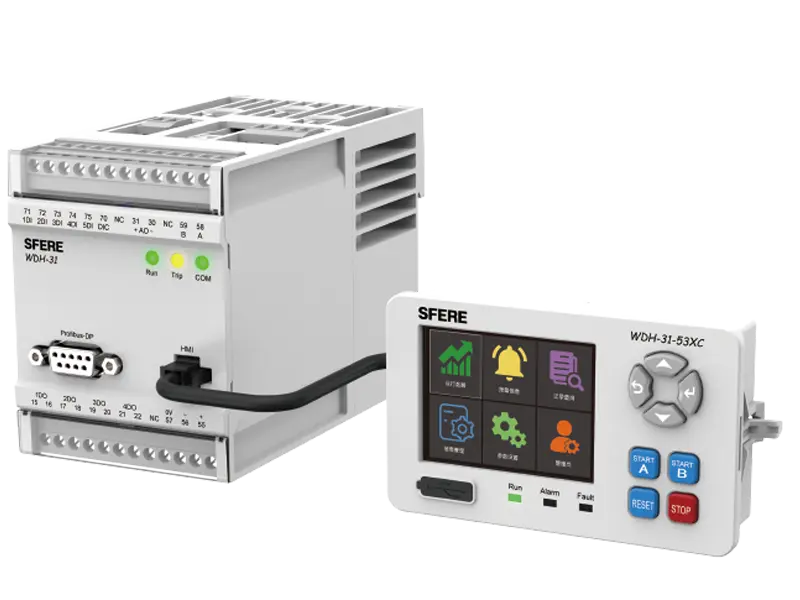
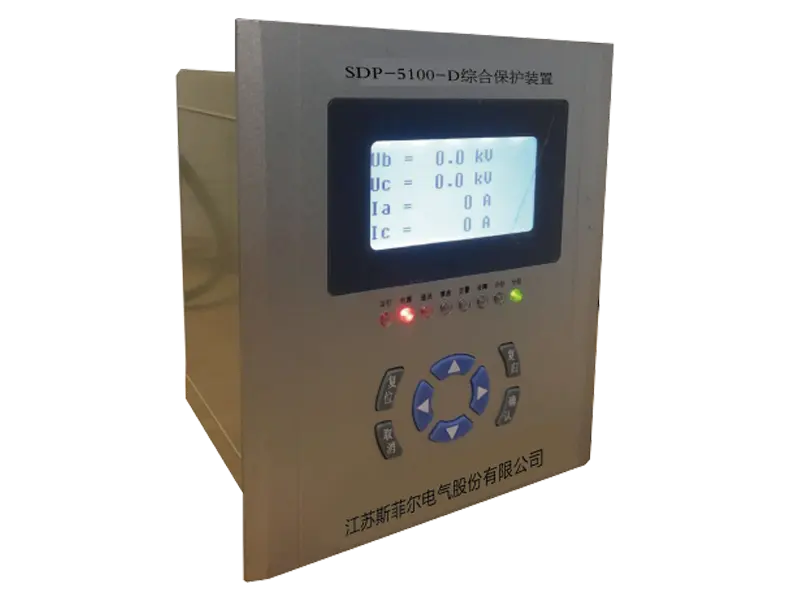
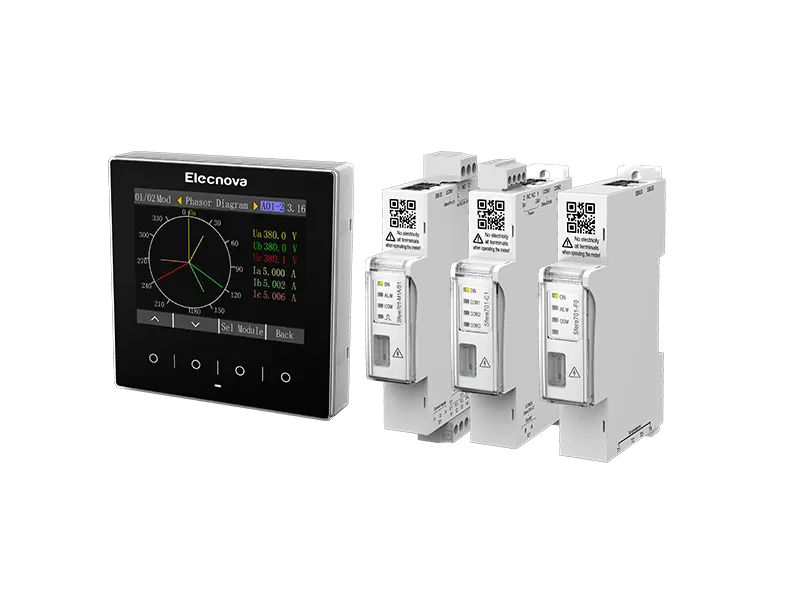
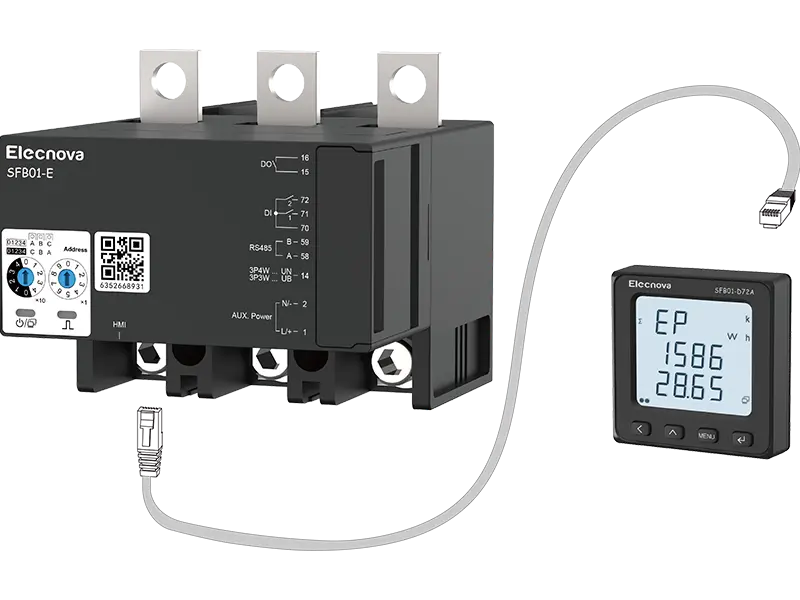
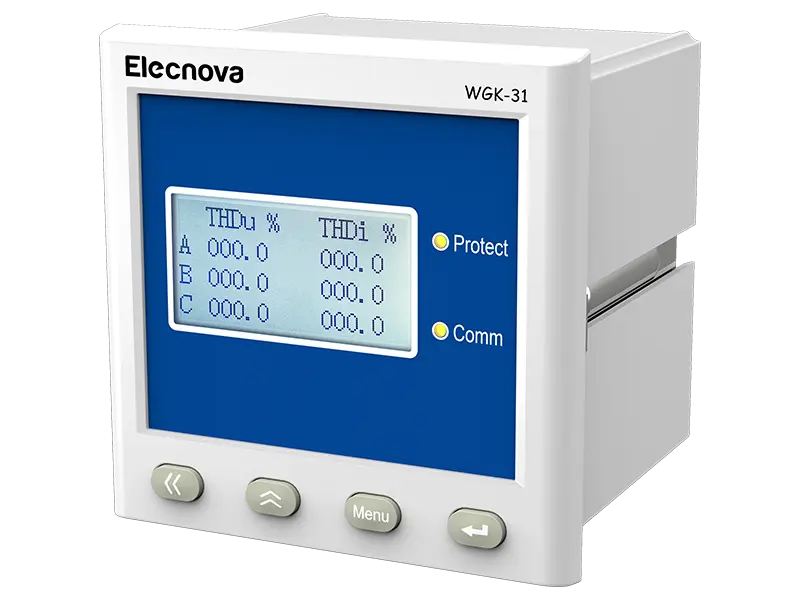
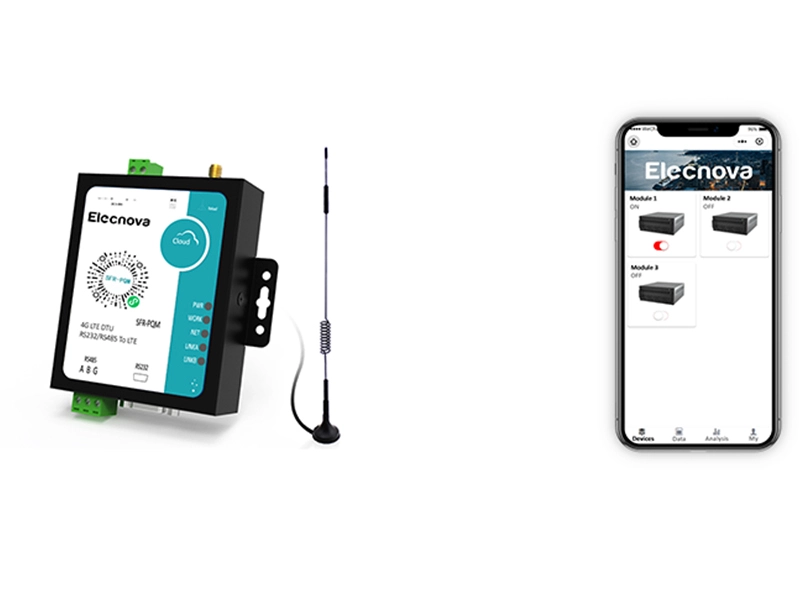
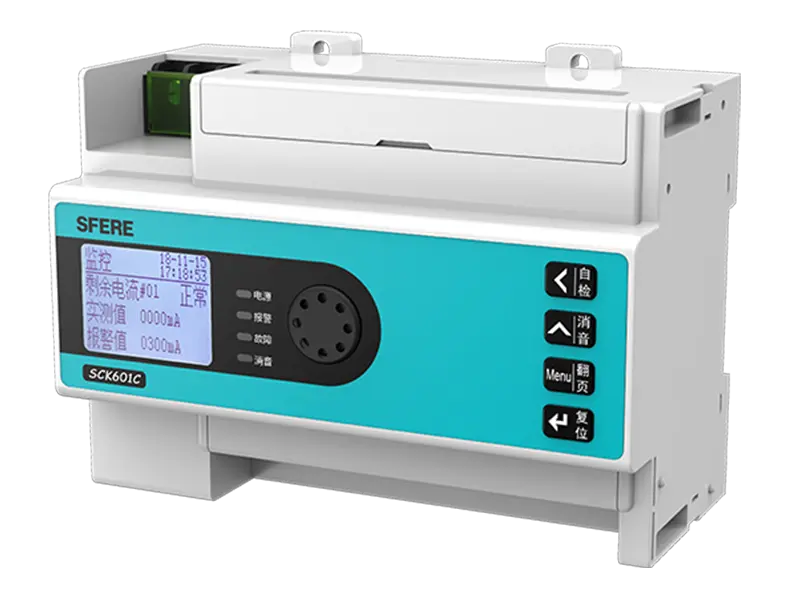
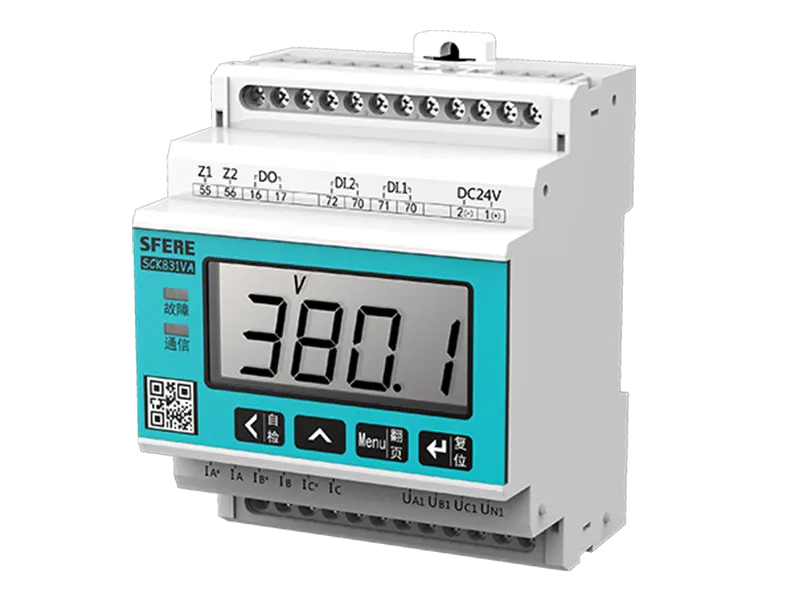
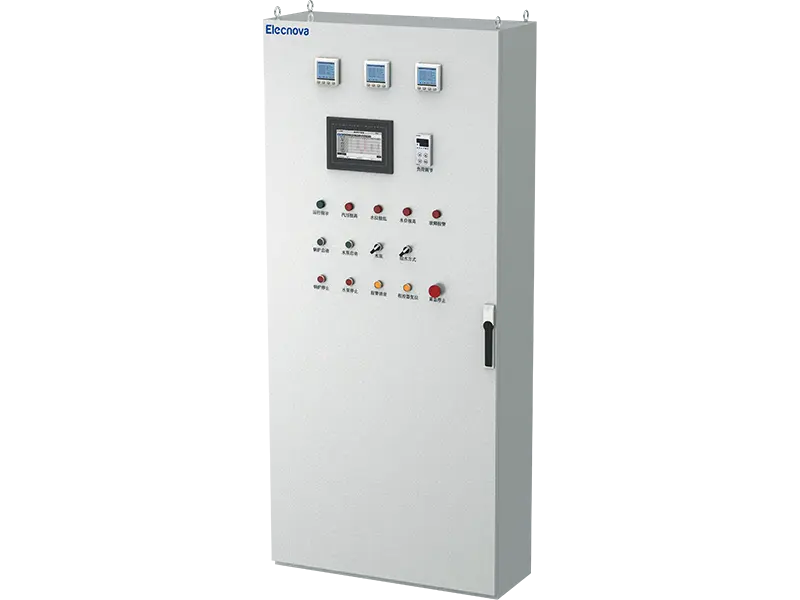
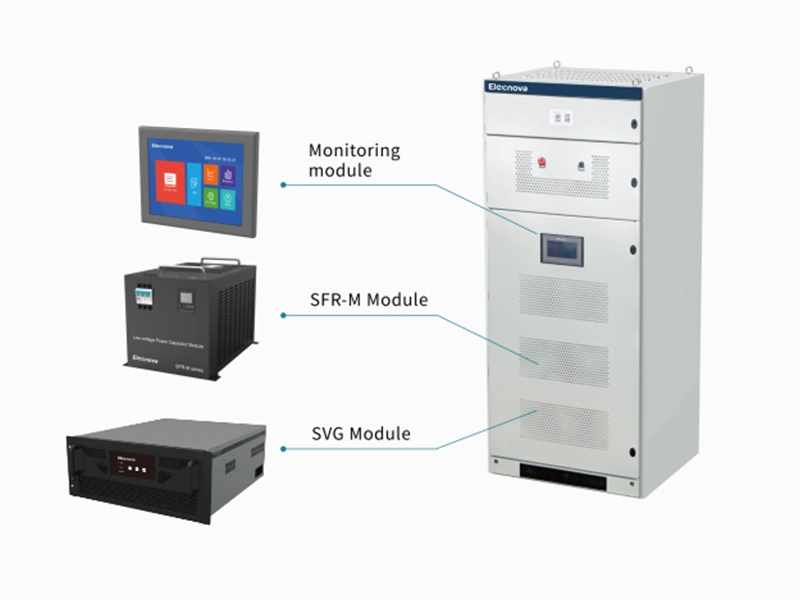
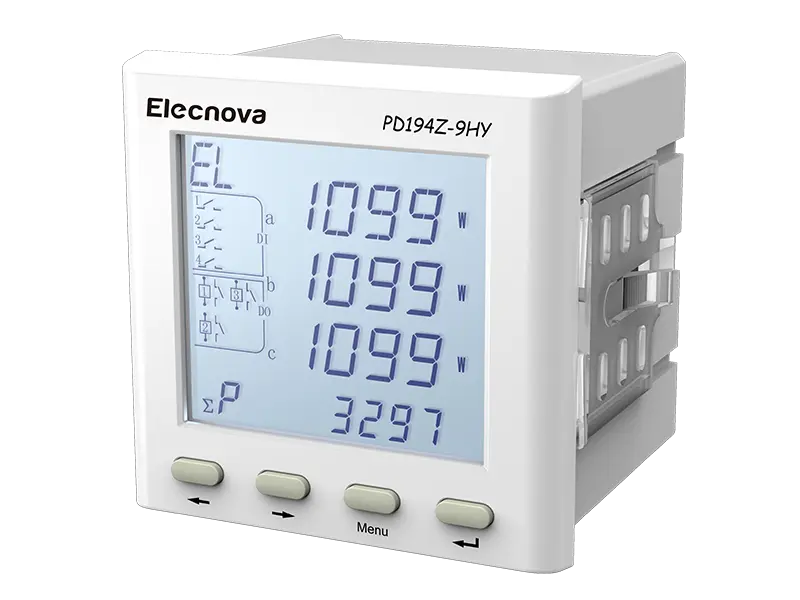
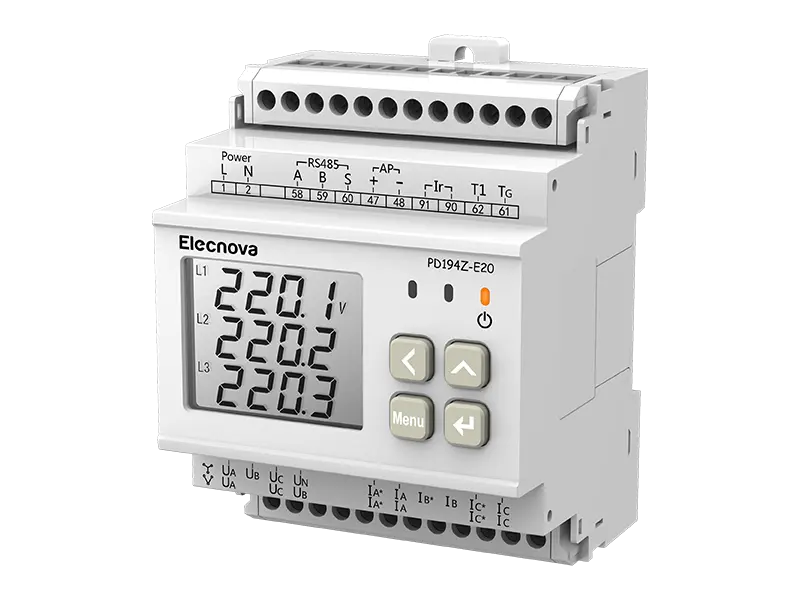
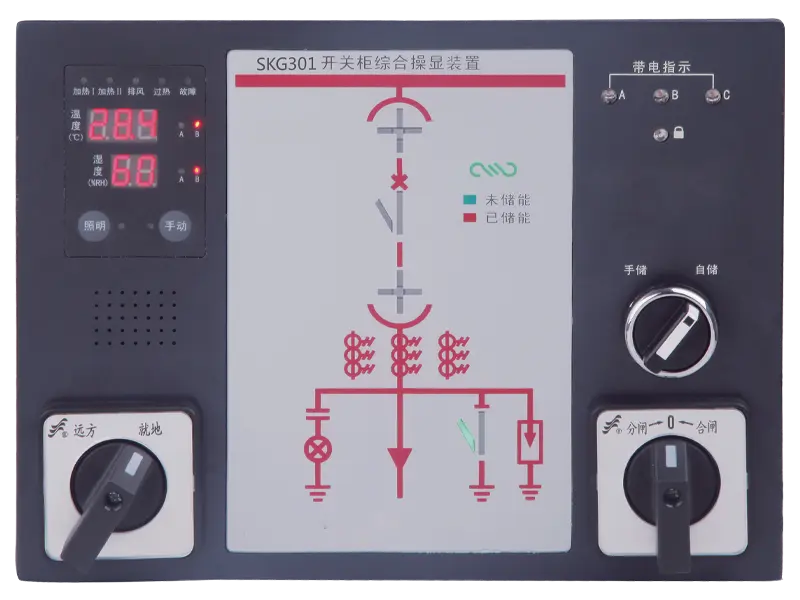
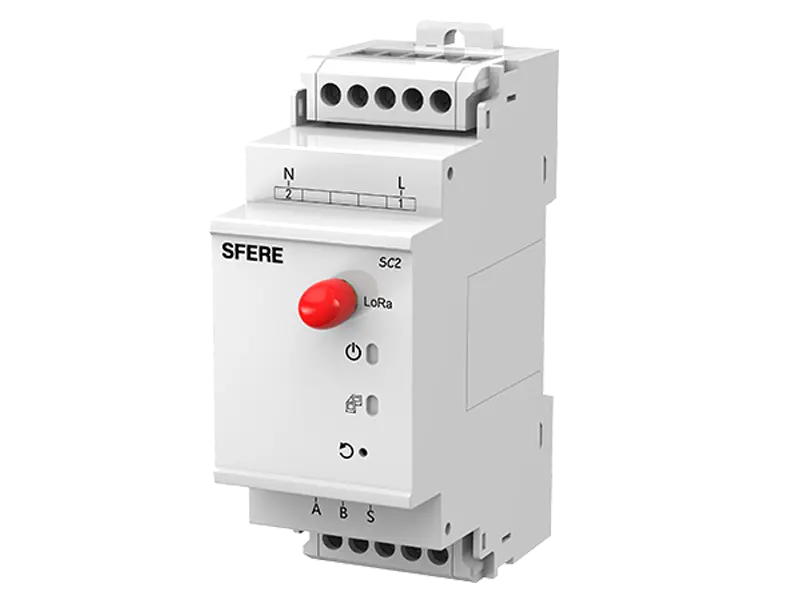
A multifunction meter is a sophisticated device used in electrical systems to measure and monitor various parameters related to power quality, energy consumption, and electrical parameters. Unlike traditional meters that measure only basic parameters like voltage, current, and power, multifunction meters offer a wide range of functionalities, making them versatile tools for monitoring and managing electrical systems.
Key features of multifunction meters include:
1. Measurement of Multiple Parameters: Multifunction meters can measure a wide range of electrical parameters, including voltage, current, power factor, active power (kW), reactive power (kVAR), apparent power (kVA), frequency, and harmonics. This comprehensive measurement capability provides detailed insights into the performance and efficiency of electrical systems.
2. Power Quality Monitoring: Multifunction meters are equipped with advanced features to monitor power quality parameters such as voltage fluctuations, voltage sags and swells, harmonics, and total harmonic distortion (THD). Monitoring power quality helps identify issues that can affect the performance of electrical equipment and sensitive electronic devices.
3. Energy Management: Multifunction meters track energy consumption in real-time, allowing users to monitor and analyze energy usage patterns. This information helps identify opportunities for energy efficiency improvements, optimize energy usage, and reduce costs.
4. Data Logging and Communication: Many multifunction meters feature built-in data logging capabilities, allowing them to record historical data for analysis and reporting purposes. Additionally, they often support communication protocols such as Modbus, Ethernet, or Profibus, enabling integration with building management systems, SCADA systems, or other monitoring platforms.
5. Alarming and Notification: Multifunction meters can be programmed to trigger alarms or notifications based on predefined thresholds or conditions. This enables proactive monitoring of electrical systems and helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate.
6. Remote Monitoring and Control: Some advanced multifunction meters support remote monitoring and control capabilities, allowing users to access real-time data and control functions remotely via a computer, smartphone, or web interface.
Overall, multifunction meters play a crucial role in modern electrical systems by providing comprehensive monitoring, analysis, and control capabilities. They are essential tools for ensuring power quality, optimizing energy efficiency, and maintaining reliable operation of electrical infrastructure in various applications, including industrial facilities, commercial buildings, and renewable energy installations.