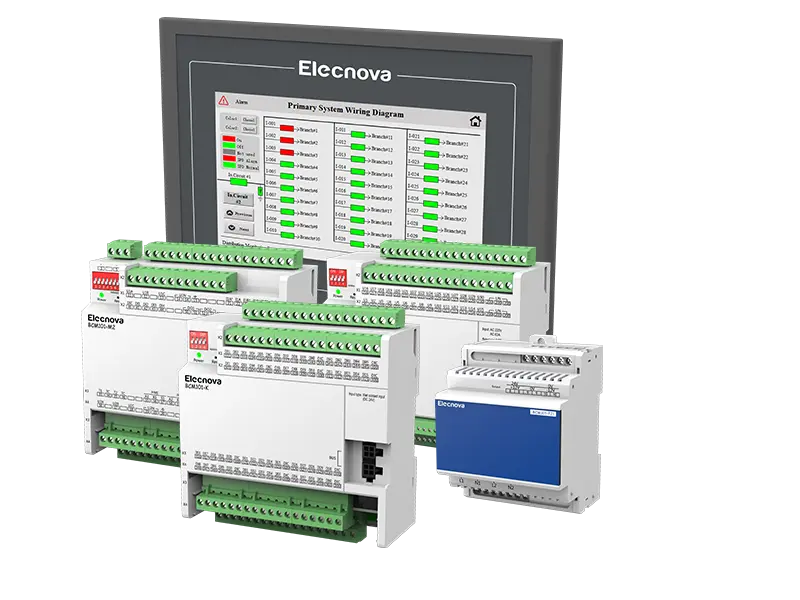
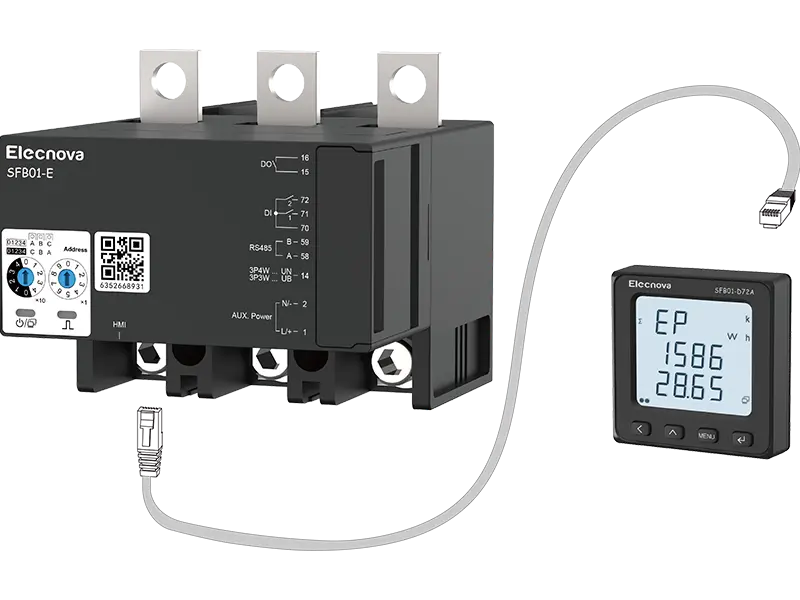
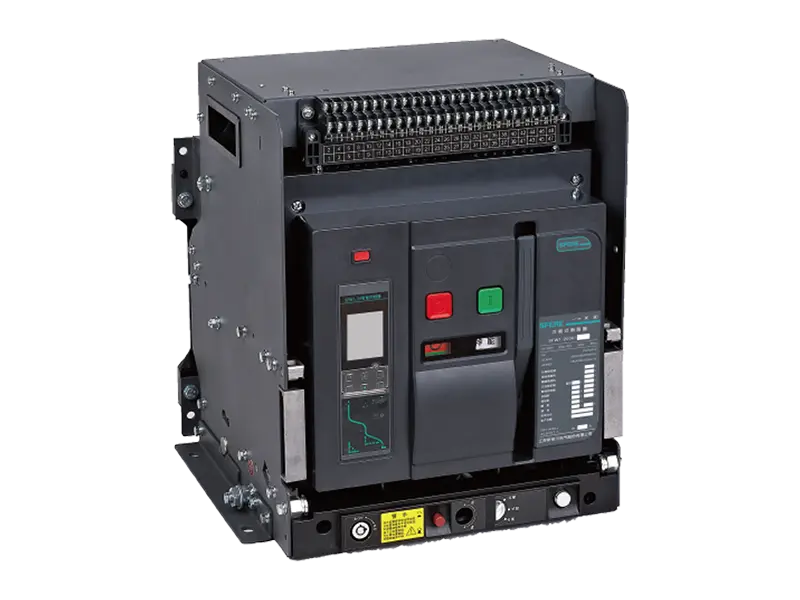
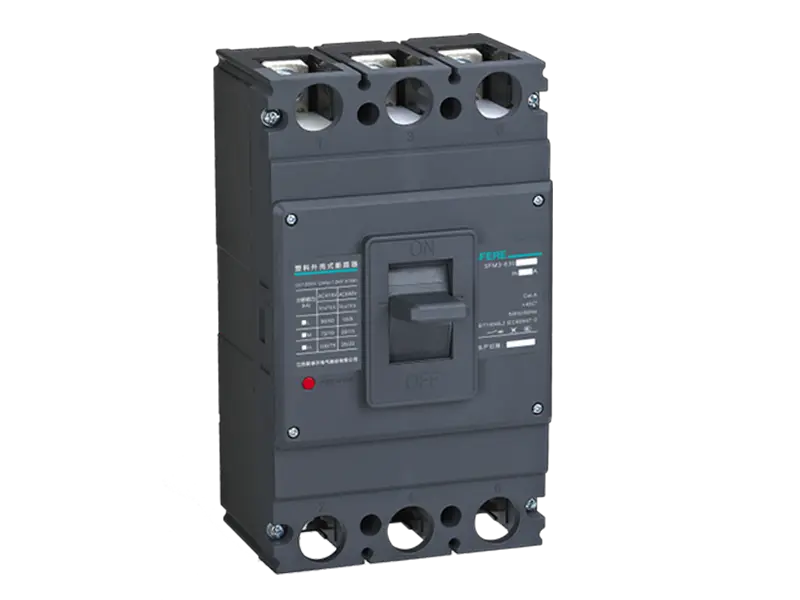
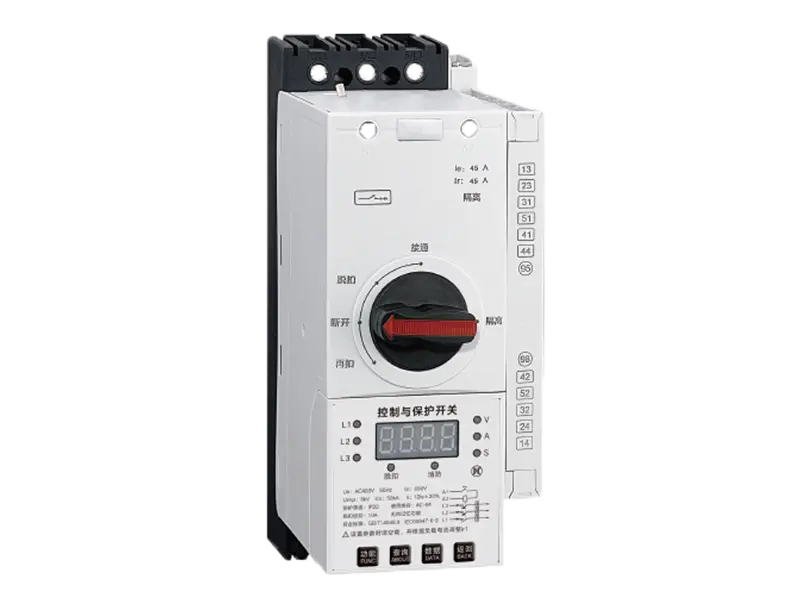
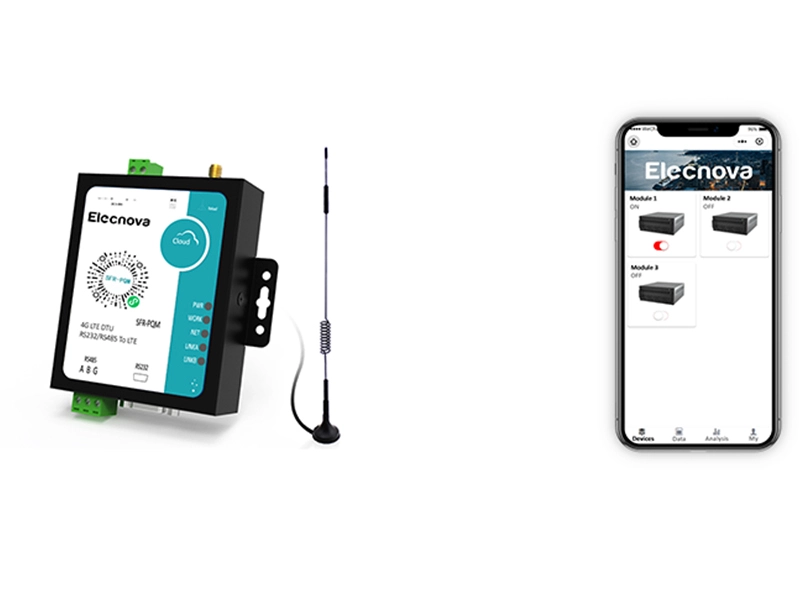
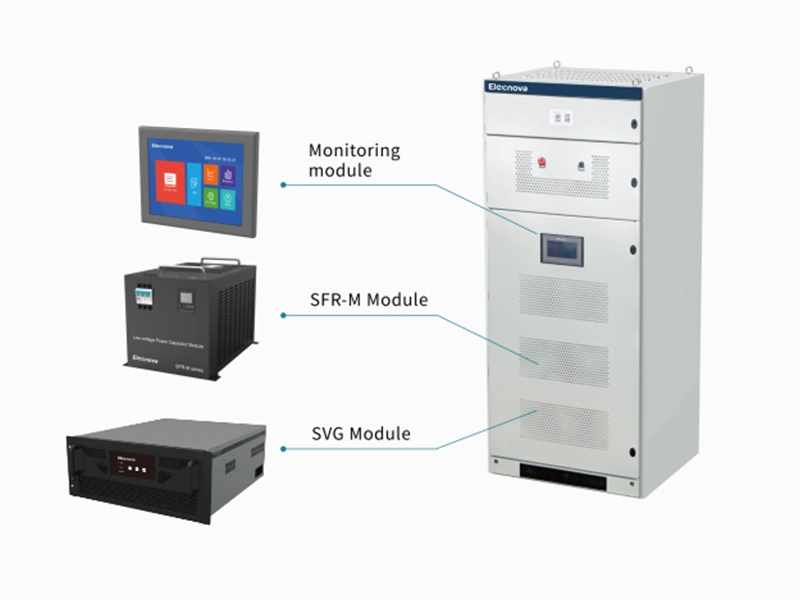
A communication gateway serves as an interface between different networks, protocols, or devices, facilitating communication and data exchange between them. It acts as a bridge, translator, or mediator to enable seamless interoperability and integration in diverse technological environments.
Key aspects and functions of communication gateways include:
1. Protocol Translation: Communication gateways translate data between different communication protocols, such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP, and MQTT, allowing devices using different protocols to communicate effectively.
2. Network Interconnection: Gateways connect devices or networks operating on different physical or logical networks, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, cellular, or serial connections, enabling communication across heterogeneous networks.
3. Data Format Conversion: Gateways convert data formats between systems or applications, ensuring compatibility and consistency in data representation, encoding, and formatting.
4. Data Filtering and Aggregation: Gateways filter and aggregate data from multiple sources or devices before forwarding it to the destination, optimizing bandwidth usage and reducing network congestion.
5. Security and Access Control: Gateways implement security measures such as encryption, authentication, and access control to secure data transmission and protect against unauthorized access or malicious attacks.
6. Routing and Routing Control: Gateways route data packets between networks or devices based on predefined rules or routing tables, ensuring efficient and reliable data transmission.
7. Protocol Conversion: In industrial automation and IoT applications, gateways convert fieldbus protocols (e.g., Modbus RTU, Profibus DP) to higher-level protocols (e.g., Modbus TCP/IP, MQTT) for seamless integration with higher-level systems or cloud platforms.
8. Data Transformation and Enrichment: Gateways may perform data transformation, enrichment, or preprocessing tasks, such as data normalization, filtering, aggregation, or calculation, to prepare data for further analysis or processing.
Overall, communication gateways play a crucial role in enabling interoperability, integration, and connectivity in complex and heterogeneous environments, allowing diverse systems, devices, and networks to communicate effectively and exchange data securely. They are essential components in industrial automation, IoT, smart cities, and other interconnected systems where seamless communication and data exchange are critical for operational efficiency and innovation.