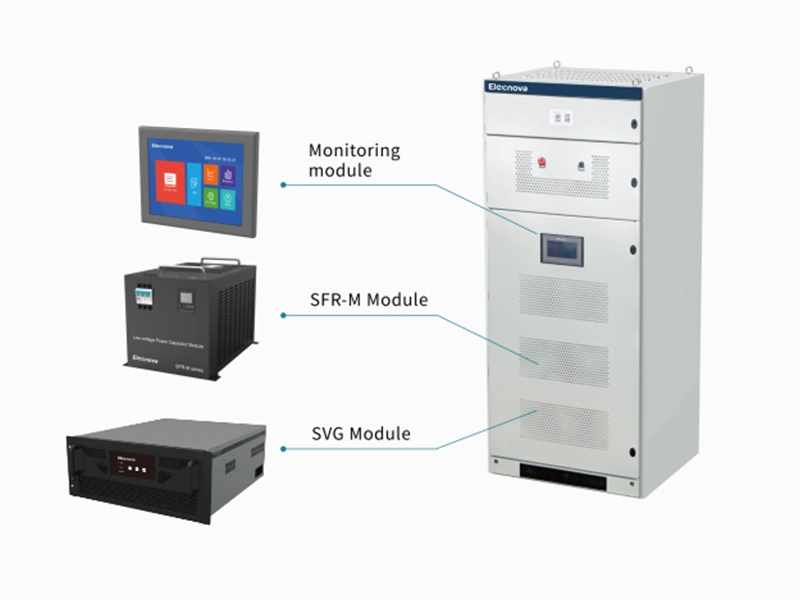
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are crucial components in electrical systems for protecting against overload, short circuit, and earth fault currents. There are several types of MCBs, each designed for specific applications and environments:
1. Type B MCB: These are the most common type of MCBs and are suitable for general domestic and commercial applications where the loads are predominantly resistive or slightly inductive.
2. Type C MCB: Type C MCBs have a higher magnetic trip threshold compared to Type B, making them suitable for applications with moderate inrush currents or loads with higher inrush currents, such as some motors and fluorescent lighting.
3. Type D MCB: Type D MCBs have even higher magnetic trip thresholds and are suitable for applications with high inrush currents or loads with very high inrush currents, such as large motors, transformers, and discharge lighting.
4. Type K MCB: These are designed specifically for use with capacitive loads, such as fluorescent lighting with electronic ballasts.
5. Type Z MCB: Type Z MCBs have a very sensitive earth leakage protection and are designed for use in circuits where protection against electric shock is critical, such as in medical locations or areas with sensitive electronic equipment.
6. Selective MCBs: These MCBs are designed to coordinate with each other in a circuit to ensure that only the MCB closest to the fault trips, minimizing the impact of the fault and maximizing the availability of the rest of the circuit.
7. Motor Protection MCBs: These MCBs are specifically designed to provide overload and short-circuit protection for motors. They often include features such as adjustable overload settings and phase-failure protection.
These are some of the common types of MCBs available, each serving specific purposes in electrical installations. The choice of MCB type depends on factors such as the nature of the load, the environment, and the level of protection required.